Can Epilepsy Be Cured with Surgery? Exploring Success Rates and Procedures
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent, unprovoked seizures that can significantly affect a person’s daily life. While medication is often the first line of treatment, approximately one-third of epilepsy patients continue to experience seizures despite medical therapy. For these individuals, surgery can be a powerful and potentially curative option. In this blog, we’ll explore the types of epilepsy surgery, success rates, risks, and why choosing an experienced specialist like Dr. Adam Amrudeen can make all the difference.
Understanding Epilepsy and When Surgery Becomes an Option
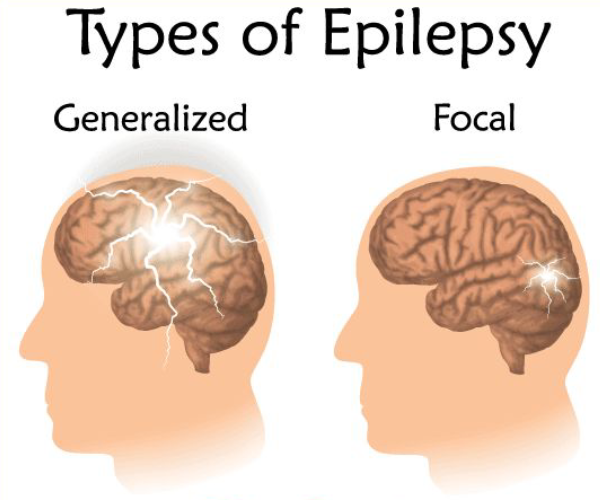
Epilepsy arises from abnormal electrical activity in the brain, causing seizures that vary in intensity and symptoms. For many, seizures can be managed with medication, but some people have a type of epilepsy that doesn’t respond well to drugs. When medication proves ineffective, doctors may consider surgical options, which are designed to either remove or alter brain tissue to control seizures.
Surgery is generally only recommended when:
- Medication is Ineffective: If patients have tried two or more antiepileptic drugs with limited results.
- Seizures Are Debilitating: For patients with severe seizures that interfere with quality of life.
- Epilepsy Has a Specific Origin in the Brain: Surgical success is higher if seizures come from one focal area that can be safely removed or modified.
Types of Epilepsy Surgeries
-
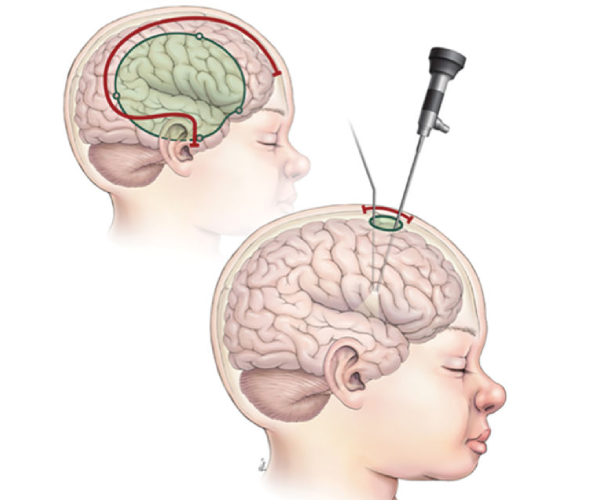
Resective Surgery
The most common form of epilepsy surgery, resective surgery involves removing the part of the brain responsible for seizures. For focal epilepsy, this procedure often focuses on the temporal lobe (temporal lobectomy), which has shown high success rates.
-
Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy (LITT)
A minimally invasive technique using laser technology to target and destroy seizure-causing brain tissue. This method is less invasive than open surgery and has a shorter recovery time.
-
Corpus Callosotomy
This procedure disconnects the corpus callosum, which is the part of the brain that allows the two hemispheres to communicate. While it doesn’t cure epilepsy, it reduces the severity of seizures, particularly in patients with drop seizures.
-
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS)
VNS involves implanting a device that stimulates the vagus nerve to reduce seizure frequency. It’s often used in patients who aren’t suitable candidates for brain surgery.
-
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
DBS involves placing electrodes in specific brain regions to regulate abnormal electrical activity. It’s primarily used for patients who don’t respond to other surgical options.
-
Responsive Neurostimulation (RNS)
RNS is a more personalized approach, as it involves implanting a device that detects seizure activity in real time and sends electrical impulses to interrupt the seizure before it starts.
Each surgical option has unique benefits and risks, and the choice of surgery depends on the type and origin of the epilepsy, as well as the patient’s health profile and surgical candidacy.
Success Rates of Epilepsy Surgery
Epilepsy surgery has shown encouraging success rates, especially for patients with focal epilepsy. Success rates vary by procedure:
- Temporal Lobe Surgery: Temporal lobectomy, one of the most common surgeries, has success rates between 60-80% for complete seizure freedom. This surgery is most effective for patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy.
- Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy (LITT): LITT has shown seizure control rates around 50-70%, making it an effective option for some patients who want a minimally invasive approach.
- Corpus Callosotomy: This surgery has a high success rate for reducing drop attacks, often around 70-90%, though it rarely eliminates all seizure activity.
- Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) and Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): Both techniques have success rates of around 50-60% for seizure reduction, but they are usually not curative.
- Responsive Neurostimulation (RNS): RNS can reduce seizures by 50% or more, although complete seizure freedom is less common.
- Improvement in Quality of Life: Success in epilepsy surgery is often measured not only by the reduction in seizure frequency but also by the improvement in quality of life. A successful outcome often allows patients to experience greater independence and reduced reliance on medication.
Success in epilepsy surgery is often measured not only by the reduction in seizure frequency but also by the improvement in quality of life. A successful outcome often allows patients to experience greater independence and reduced reliance on medication.
Risks and Considerations in Epilepsy Surgery
Like all surgeries, epilepsy surgery comes with risks, and it’s essential for patients and their families to understand them before proceeding. Common risks include:
-
Infection:
While generally low, there’s a risk of infection, especially with implantable devices.
-
Cognitive Changes
Memory and language abilities can be affected, particularly in temporal lobe surgeries.
-
Psychiatric Effects:
Some patients may experience mood changes or depression post-surgery, which should be monitored and treated as needed.
-
Neurological Deficits:
Depending on the area of surgery, patients may face weakness, vision changes, or sensory deficits, although such cases are rare.
Recovery and Follow-Up After Surgery
Recovery times vary depending on the type of surgery. Traditional resective surgeries often require a hospital stay of several days, with full recovery taking several weeks. Minimally invasive procedures like LITT typically have a shorter recovery period. Long-term follow-up is essential, as patients may still need medication, even if they are seizure-free, and regular monitoring ensures any post-surgery complications are managed promptly.
Why Choose Surgery? A Life-Changing Decision
For many patients, epilepsy surgery provides an opportunity to regain control over their lives. Patients who achieve seizure freedom or significant seizure reduction often report improved mood, higher quality of life, and increased independence. Surgery isn’t for everyone, but for patients who qualify, it offers a chance to escape the limitations imposed by recurrent seizures.
Dr. Adam Amrudeen: The Expert in Epilepsy Surgery
When considering epilepsy surgery, it’s crucial to consult a specialist with a deep understanding of the complexities of this condition. Dr. Adam Amrudeen is a highly skilled and compassionate expert in epilepsy surgery. With years of experience and numerous successful cases, Dr. Amrudeen combines expertise with a patient-centered approach, ensuring each patient receives personalized care tailored to their unique needs. His comprehensive knowledge of the latest techniques and dedication to patient safety make him an ideal choice for anyone considering epilepsy surgery.
If you or a loved one is living with drug-resistant epilepsy, consult Dr. Adam Amrudeen to explore your options. With his guidance, you can make an informed decision that prioritizes your health and quality of life.

Dr. Adam Kamrudeen
Neurosurgeon in Navi Mumbai
- MBBS, MS – General Surgery,
- MCh – Neuro Surgery
- Brain & Spine Surgeon in Navi Mumbai
Conclusion
Consulting with Dr. Adam Kamrudeen, a skilled neurosurgeon in Navi Mumbai, is crucial if you're dealing with spondylosis. This degenerative condition of the spine can cause significant pain and mobility issues. Dr. Adam Kamrudeen will assess your condition and explain the surgical and non-surgical treatment options available, including minimally invasive techniques to relieve pain and restore function.
